Docker Installation#
n8n recommends using Docker for most self-hosting needs. It provides a clean, isolated environment, avoids operating system and tooling incompatibilities, and makes database and environment management simpler.
You can also use n8n in Docker with Docker Compose. You can find Docker Compose configurations for various architectures in the n8n-hosting repository.
Self-hosting knowledge prerequisites
Self-hosting n8n requires technical knowledge, including:
- Setting up and configuring servers and containers
- Managing application resources and scaling
- Securing servers and applications
- Configuring n8n
n8n recommends self-hosting for expert users. Mistakes can lead to data loss, security issues, and downtime. If you aren't experienced at managing servers, n8n recommends n8n Cloud.
You can also follow along with our video guide here:
Prerequisites#
Before proceeding, install Docker:
- Docker Desktop is available for Mac, Windows, and Linux. Docker Desktop includes the Docker Engine and Docker Compose.
- Docker Engine and Docker Compose are also available as separate packages for Linux. Use this for Linux machines without a graphical environment or when you don't want the Docker Desktop UI.
Stable and Beta versions
n8n releases a new minor version most weeks. The stable version is for production use. beta is the most recent release. The beta version may be unstable. To report issues, use the forum.
Current stable: 2.6.3
Current beta: 2.7.1
Starting n8n#
From your terminal, run the following commands, replacing the <YOUR_TIMEZONE> placeholders with your timezone:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | |
This command creates a volume to store persistent data, downloads the required n8n image, and starts the container with the following settings:
- Maps and exposes port
5678on the host. - Sets the timezone for the container:
- the
TZenvironment variable sets the system timezone to control what scripts and commands likedatereturn. - the
GENERIC_TIMEZONEenvironment variable sets the correct timezone for schedule-oriented nodes like the Schedule Trigger node.
- the
- Enforces secure file permissions for the n8n configuration file.
- Enables task runners, the recommended way of executing tasks in n8n.
- Mounts the
n8n_datavolume to the/home/node/.n8ndirectory to persist your data across container restarts.
Once running, you can access n8n by opening: http://localhost:5678
Using with PostgreSQL#
By default, n8n uses SQLite to save credentials, past executions, and workflows. n8n also supports PostgreSQL, configurable using environment variables as detailed below.
Persisting the .n8n directory still recommended
When using PostgreSQL, n8n doesn't need to use the .n8n directory for the SQLite database file. However, the directory still contains other important data like encryption keys, instance logs, and source control feature assets. While you can work around some of these requirements, (for example, by setting the N8N_ENCRYPTION_KEY environment variable), it's best to continue mapping a persistent volume for the directory to avoid potential issues.
To use n8n with PostgreSQL, execute the following commands, replacing the placeholders (depicted within angled brackets, for example <POSTGRES_USER>) with your actual values:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | |
You can find a complete docker-compose file for PostgreSQL in the n8n hosting repository.
Updating#
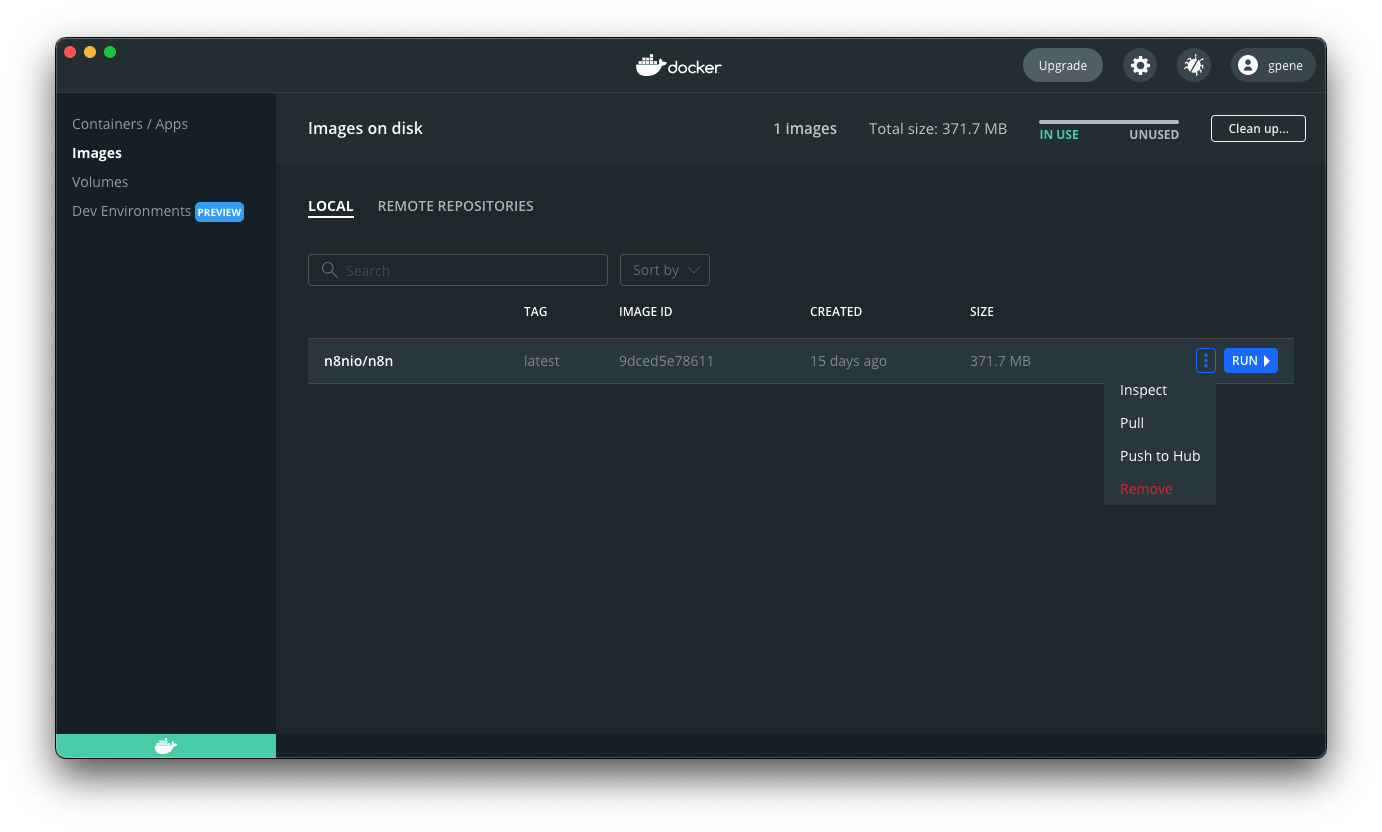
To update n8n, in Docker Desktop, navigate to the Images tab and select Pull from the context menu to download the latest n8n image:
You can also use the command line to pull the latest, or a specific version:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
After pulling the updated image, stop your n8n container and start it again. You can also use the command line. Replace <container_id> in the commands below with the container ID you find in the first command:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | |
Updating Docker Compose#
If you run n8n using a Docker Compose file, follow these steps to update n8n:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | |
n8n with tunnel#
Danger
Use this for local development and testing. It isn't safe to use it in production.
To use webhooks for trigger nodes of external services like GitHub, n8n has to be reachable from the web. n8n runs a tunnel service that can redirect requests from n8n's servers to your local n8n instance.
Start n8n with --tunnel by running:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | |
Next steps#
- Find more information about Docker setup in the README file for the Docker image.
- Learn more about configuring and scaling n8n.
- Or explore using n8n: try the Quickstarts.